APPLICATIONS
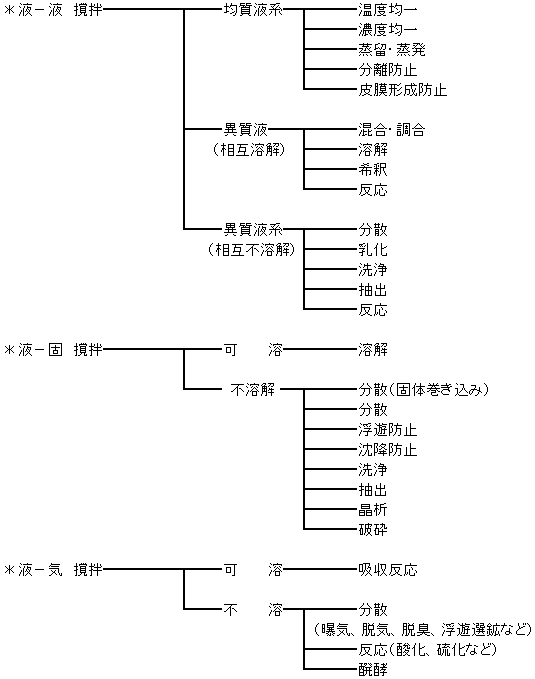
Agitation forms include liquid-liquid, liquid-solid, and liquid-vapor. The figure below describes the main purposes of agitation for each agitation form.
Agitation forms and purposes
Typical application fields and applications
Agitation operations are used in many products we see and in many places associated with our lives. Some of them are listed below.
Agitators function as devices that handle important roles in each of their installation locations.
| General chemical industry | Preparation, reaction, etc. of chemical solutions such as acids and alkalis |
| Petroleum industry | Preparation, reaction, etc. of hydrocarbon liquids, asphalt, lubricating oils, etc. |
| Resin industry | Polymerization reaction, crystallization, sedimentation prevention, etc. of ABS, PTA, PVC, PP, and other resins |
| Rubber industry | Rubber dissolution, homogeneous mixing, etc. |
| Adhesive industry | Rubber dissolution, homogeneous mixing, etc. |
| Painting ink industry | Varnish reaction, mixing, homogeneous mixing, material dispersion, etc. |
| Magnetic material industry | Material dispersion, preparation, and storage |
| Paper making industry | White clay dispersion, starch dispersion, steaming, paint homogeneous mixing, and valve mixing |
| Pharmaceutical industry | Preparation, etc. of chemical solutions |
| Food industry | Manufacturing, etc. of fruit juice, dairy products, seasoning, and sweets |
| Fermentation/brewing industry | Preparation etc. of sake, beer, and wine |
| Mining industry | Hydrometallurgy = metal slurry reaction, homogenization, sedimentation prevention, etc. |
| Ceramic industry | Clay dissolution, etc. |
| Environmental facilities | For flue-gas desulfurization equipment, water treatment, etc. |
| Civil engineering and construction industry | モMortar mixing, cement draining treatment, etc. |
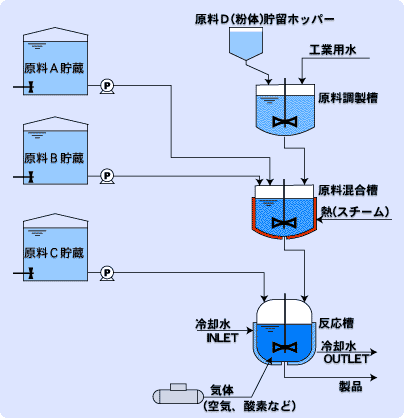
Examples of how agitator is used in a manufacturing plant